
What is a stroke?
Spasticity is a disorder that affects the muscles due to prolonged muscle contraction and is characterized by tight or stiff muscles and loss of the ability to control them.
A stroke may affect your ability to move and your muscles to contract or tense up, leading to stiffness and tightness, it may appear after a couple of days after the stroke or show up after weeks, months or even years later.
Untreated spasticity increases healthcare costs by as much as 400%, severe spasticity also increases the likelihood of living in an institution because of the difficulty of attending daily activities.
Do you experience any sign of spasticity?
Spasticity can take many forms. These are some of the most common:
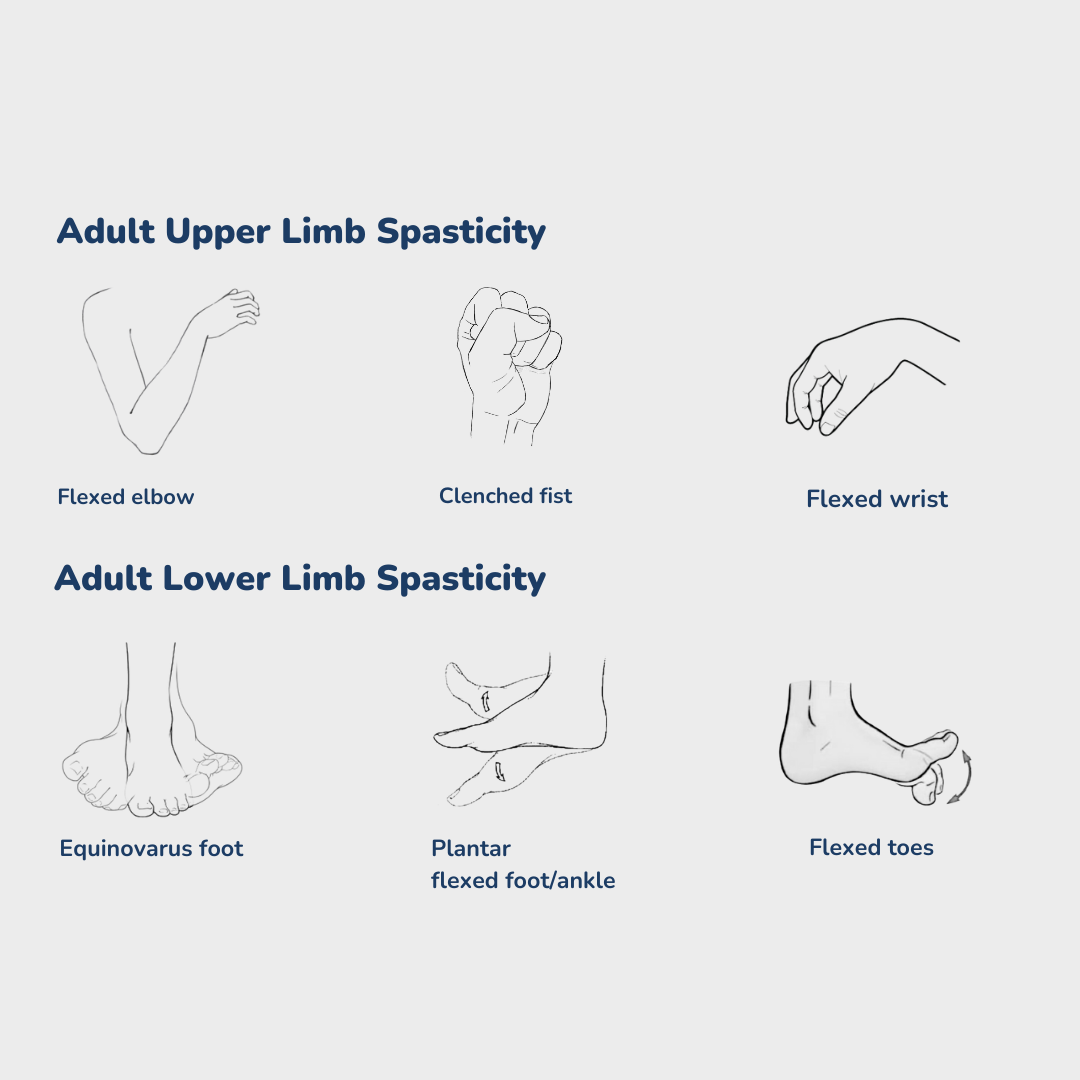
Why does spasticity happen post stroke?
In a healthy brain and nervous system, signals along nerves instruct muscles when to tighten or to relax. People with spasticity have essentially lost some of the communication between the brain, the spinal cord, and the muscles, which causes the muscles to contract or remain contracted, even when it is not desired or useful.
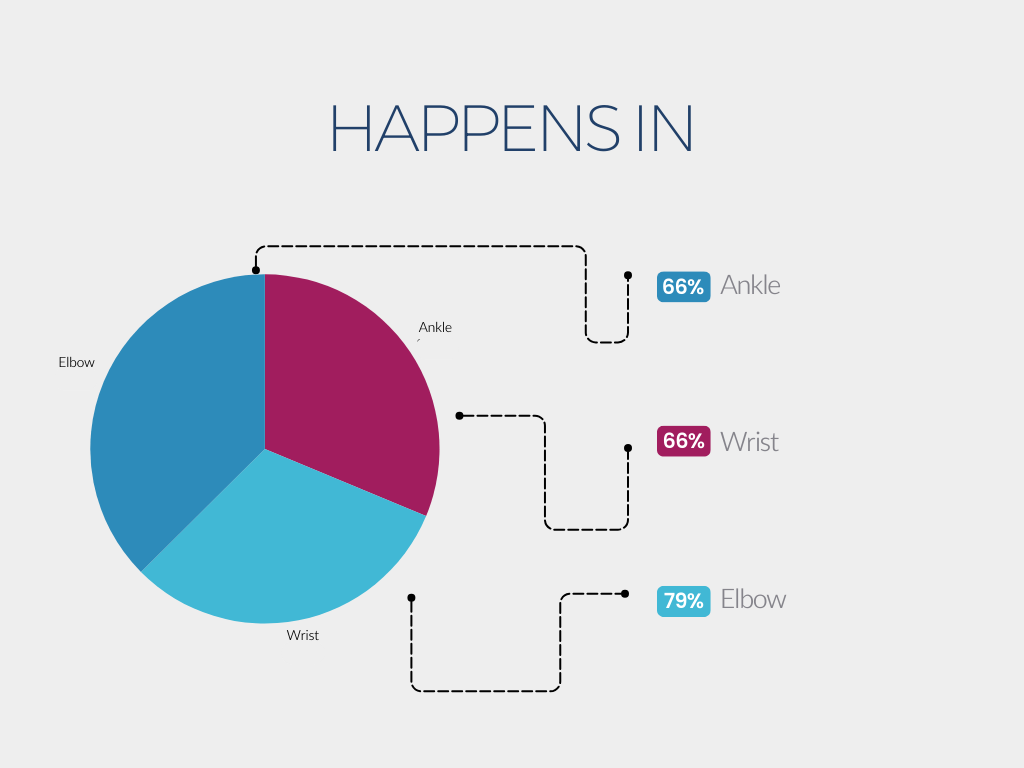
About 25% to 43% of survivors will have spasticity in the first year after their stroke.
We're here to provide support and information every step of the way.
Discover more about spasticity by clicking here.
You can book an appointment with a specialized doctor to treat your spasticity from the doctor directory.
