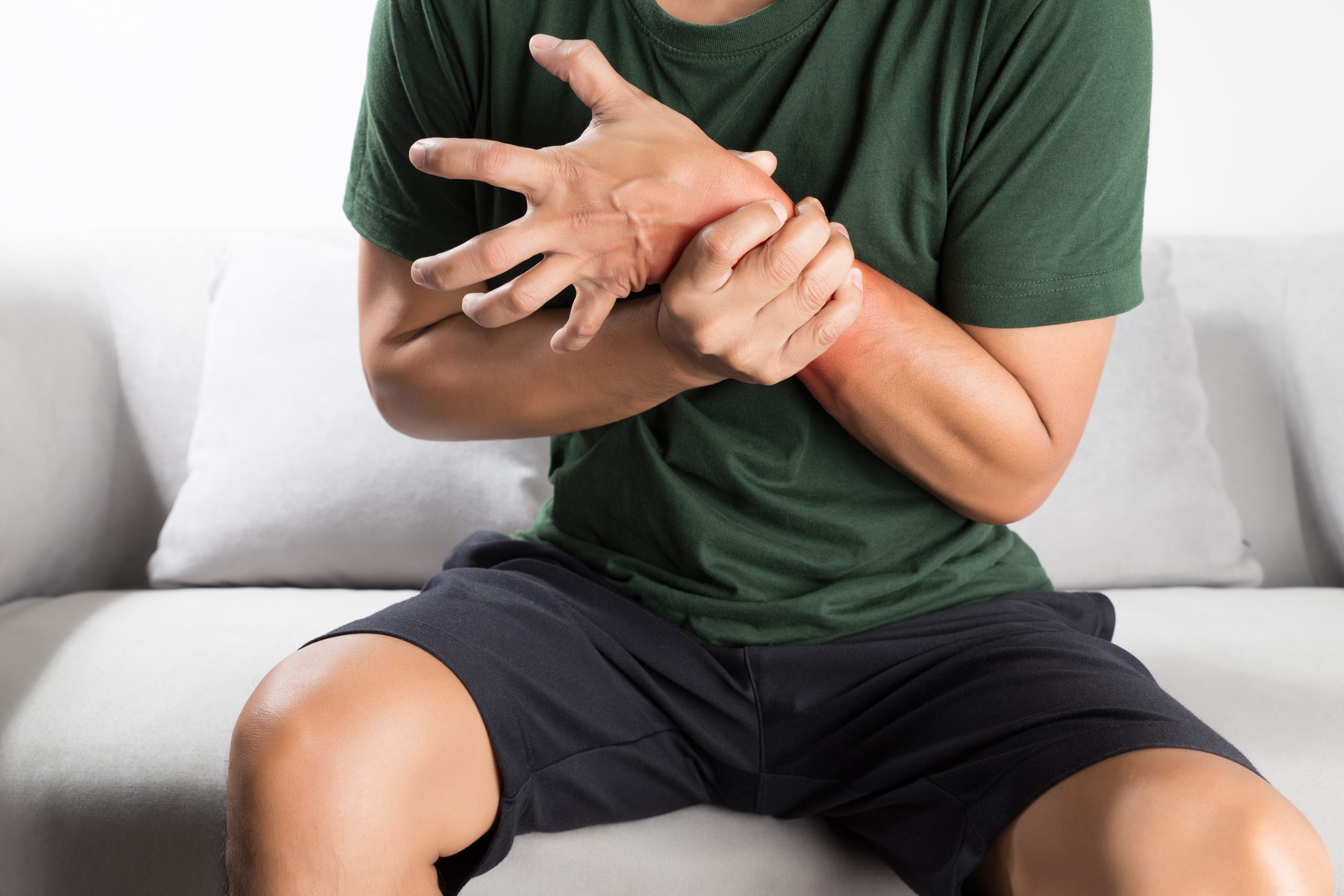

What is spasticity?
Spasticity is a disorder that affects the muscles due to prolonged muscle contraction and is characterized by tightness or stiffness in the muscles and a loss of the ability to control them.
How does that happen?
Muscles stiffen or tighten, preventing normal fluid movement which causes the muscles to remain contracted and resist being stretched, ranging in severity thus affecting movement, speech and gait.
It could be a symptom associated with a damage to the brain, spinal cord or motor nerves, and it is seen in individuals with neurological conditions.
How does that happen?
Muscles stiffen or tighten, preventing normal fluid movement which causes the muscles to remain contracted and resist being stretched, ranging in severity thus affecting movement, speech and gait.
It could be a symptom associated with a damage to the brain, spinal cord or motor nerves, and it is seen in individuals with neurological conditions.
Why does spasticity happen?
In a healthy brain and nervous system, signals travel through nerves to instruct muscles when to tighten and when to relax.
But people with spasticity have essentially lost some of the communication between the brain, the spinal cord, and the muscles, causing certain muscles to contract or remain contracted, even when it is not desired or useful.
Spasticity can be painful and affect the daily life activities of the individuals. It can interfere with their movement and daily functions, making it difficult to walk, speak, and perform daily tasks.
But people with spasticity have essentially lost some of the communication between the brain, the spinal cord, and the muscles, causing certain muscles to contract or remain contracted, even when it is not desired or useful.
Spasticity can be painful and affect the daily life activities of the individuals. It can interfere with their movement and daily functions, making it difficult to walk, speak, and perform daily tasks.
When should I see my doctor?
Treatment will be based on the frequency and level of your spasticity, and the underlying condition that’s causing it. Contact your doctor if:
- You’re experiencing spasticity for the first time and do not know the cause.
- Your spasticity is getting more severe or is happening more frequently.
- Your spasticity has changed considerably.
- You have a frozen joint.
- You have pressure sores or red skin.
- Your level of discomfort or pain is increasing.
- You’re finding it difficult to perform everyday tasks.
Your doctor may suggest physical therapy or exercises you can do at home.
In some cases, a cast or splint may be used to prevent your muscles from
becoming too tight.
In some cases, a cast or splint may be used to prevent your muscles from
becoming too tight.

